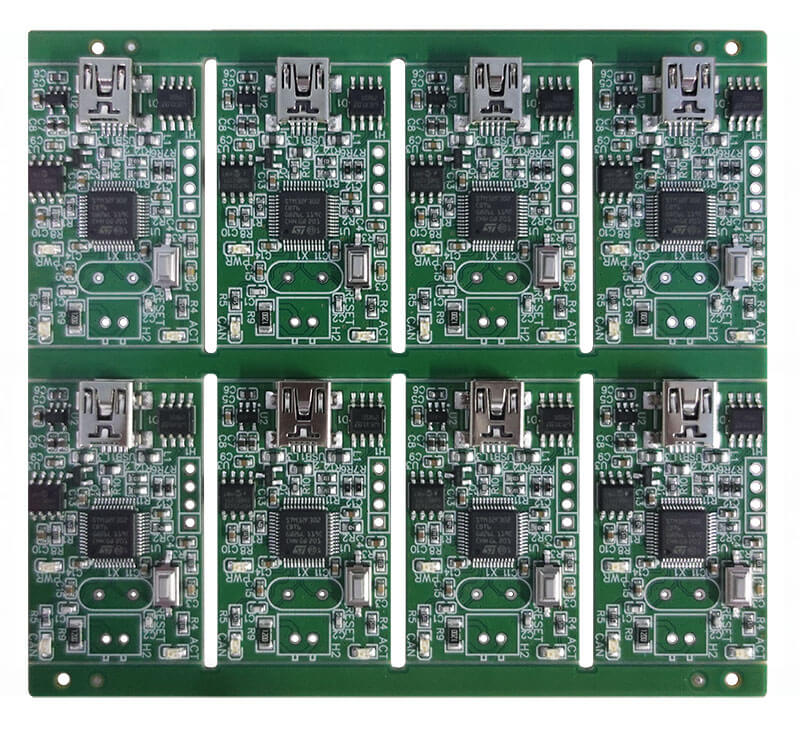
The term “rigid PCB” can make you scratch your head as you go through the world of electronics. In this ever-increasing world of electronic gadgets, the concept of rigid PCBs sounds very confusing. But do not fear, because this guide will help you in the right way.
In this article, we are going to dive deep into everything about rigid PCBs like, what they are, their constructions, the components used in their production, their applications, advantages, and so forth.
Let’s get it started.
What is Rigid PCB?
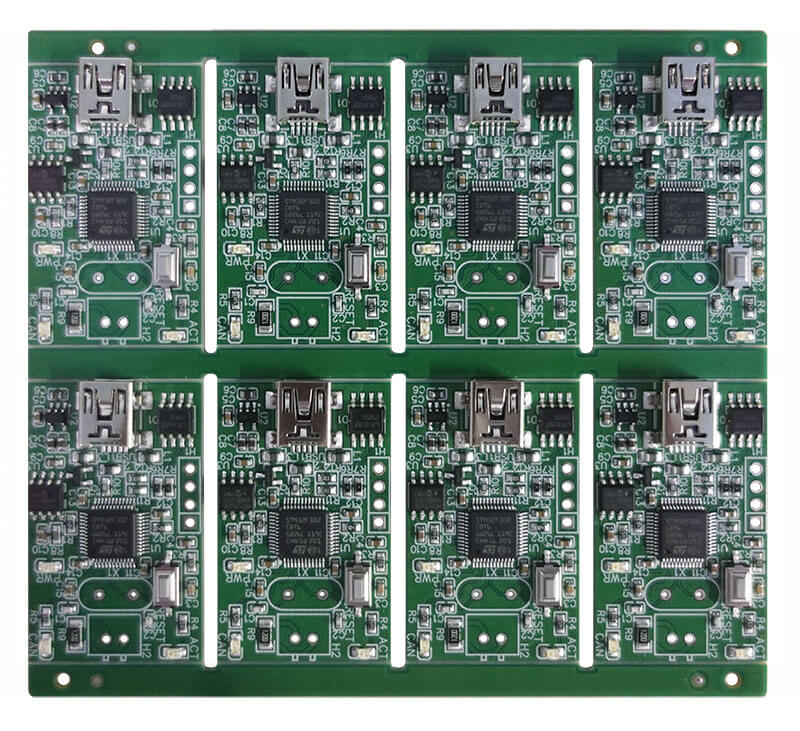
A Rigid PCB is a type of circuit board that is manufactured using rigid materials, such as fiberglass reinforced epoxy laminates. These boards give a stable and solid platform to mount electronic components and interconnections.
The design of rigid PCB typically involves a surface on the circuit board, over which the etched conductive copper traces form the electrical paths of the components.
Over and above the traces is a layer of non-conductive material, practically referred to as a solder mask.
The elements like resistor, capacitor, IC, and connector, are soldered to the board.
But what about the constructions? Let’s discuss this in detail.
Construction of Rigid PCBs
There is an exciting flair of precision engineering in constructing Rigid PCBs, where every little thing needs to be taken care of with the utmost care and detail. At the core of the Rigid PCBs is a substrate, in most cases, FR-4: a base material known as fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
This substrate serves as the foundation upon which the entire PCB is built.
Let’s understand the construction of Rigid PCBs in detail below with the help of it’s components.
Components of a Rigid PCB
The components of a Rigid PCB work together seamlessly to form the foundation of electronic devices.
Now let’s break it down to the most:
- Substrate
As said above, most times, a substrate is a fundamental base layer of a PCB, usually made of FR4 materials. It is made up of a solid base that carries the structural substrate of the circuit and an insulating member.
- Conductive Layers
On the top side of the substrate, very thin copper foils are laminated for the pathway of the conductors on the PCB to be created. The path allows the signal to go from one component to another so that the working functionality is realized with others in the circuit.
- Solder Mask
Another type of protection is a solder mask layer for the conductive paths. It is helpful in avoiding environmental influences and protecting against the formation of solder on the traces of components during the soldering operation. It additionally provides more durability and reliability for the printed circuit board.
- Silkscreen
Component designators, reference labels, and manufacturer logos are printed in the silkscreen layer or applied in the assembly, testing, and maintenance processes of the PCB.
All these parts together form a Rigid PCB, making it solid and sturdy enough for diversities of applications with electronic circuits.
The Classification of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are classified according to the number of conductive layers they possess, leading to three primary classifications:
1.Single-Sided PCBs
In these PCBs, the circuit tracks exist on only one side of the laminate. These are simple, and the cheapest kind of PCB found. They are applied mainly in situations where space and complexity are kept at a bare minimum.
The components are soldered to the other side of the traces, making them efficient for simple electronic circuits.
2.Double-Sided PCBs
On the contrary, a double-sided PCB had conductive traces on both sides of the substrate. This way, the surface area available for circuitry would practically be doubled and hence be more functional and have a higher density of components than single-sided PCBs.
The double-sided PCB suffices a great degree of versatility with a broad scope of applications, from consumer to most industrial equipment.
3.Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs are built with many layers of conductive traces sandwiched between insulating layers. This utmost level of complication and performance helps integrate delicate circuits in small architectures.
Multilayer PCBs are common in enhancing electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and medical equipment.
By classifying Rigid PCBs based on the number of conductive layers, manufacturers can tailor their designs to meet specific performance requirements and cost constraints, ensuring optimal functionality and efficiency in various applications.
Now you know the basics of Rigid PCBs, it’s time to discuss the benefits of using Rigid PCBs compared to other circuit assembly methods.
The Benefits of Using Rigid PCBs
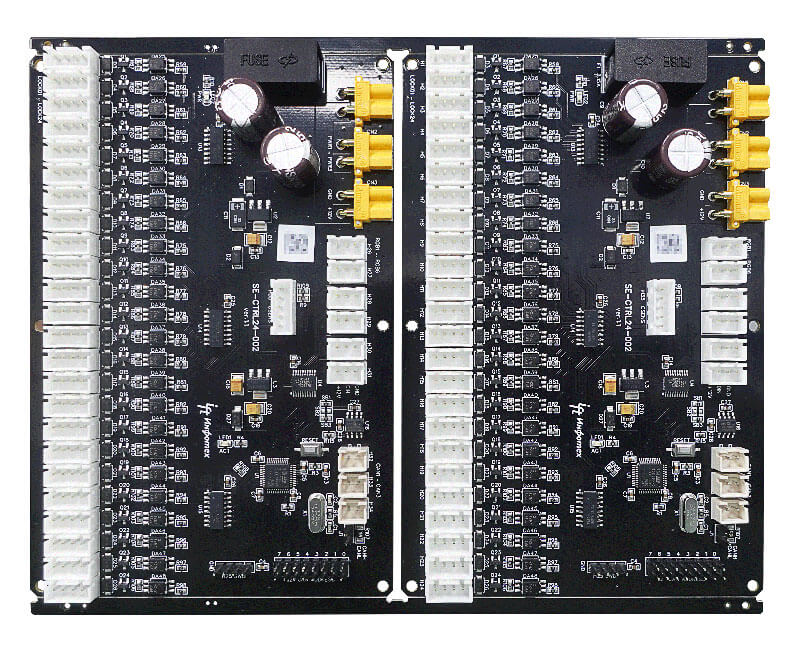
Using Rigid PCBs offers a multitude of benefits compared to alternative circuit assembly methods.
Here are some of the key advantages:
1.Cost-Effectiveness
Generally, rigid PCBs are cheaper than flex boards because of the usual way of manufacturing and the ease of material availability at the basic design level.
This cost-effectiveness makes rigid PCBs more appropriate for mass production and for prototype or low-volume applications.
2.Durable and Stable
Rigid PCBs provides a solid performance even in the harshest conditions. A rigid PCB can give a firm and strong position to all electronic parts. Applied to such parts possessing structural integrity, they will easily stand the mechanical stress and damage due to mechanical rigidity.
3.Wide Range of Manufacturing Options
Their current manufacturing infrastructure for rigid PCBs makes them better at being customized toward design requirements than soft substrates, where, for instance, the appropriate substrate material may be selected, or advanced features such as impedance control and blind vias might need to be put in place.
4.Suitable for High-Volume Production:
Rigid PCBs are scalable for high-volume production because they are efficient in fabrication and assembly mechanisms.
Therefore, this is a valid option when taking into account that most electronic devices must be produced in massive volumes, ensuring proper properties of quality and reliability.
5.Enhanced Thermal Management
Rigid PCBs have the capacity for thermal management that is better than most other mounting means.
All these will help dissipate heat properly and prevent overheating, letting the electric components perform at best, especially for the devices working at high temperatures and under heavy loads.
6.Improved Signal Integrity
The rigid structure of PCBs ensures perfect signal integrity while shaping the signal line to minimize to the greatest extent every distortion and interference factor of the signal.
It provides a positive and stable signal exchange between components. It ensures the best performance and stability of electronic devices fundamentally, mainly those with sensitive and high-speed circuitry installed.
7.Simplified Assembly and Testing
These rigid PCBs are easy to test and assemble because what has been standardized is their form and layout. Mounting components on them is simple with automated assembly equipment, hence reducing both time and costs in the production process.
Their rigidity in structure makes it very easy to test and trouble, therefore, quick identification and correction of problems in the manufacturing process.
Applications of Rigid PCBs
With their reliability, good range of use, and performance, rigid PCBs are the most preferred in manufacturing industries for electrical device production.
Here are some real-life applications:
- Computers and Laptops
They are the central part that supports the motherboard, graphic cards, and most of the circuitry within a computer or laptop, enabling people to perform simple computing to demanding applications in games and multimedia.
In most cases, these rigid printed circuit boards are used in computers and laptops. They also ensure stability and strength for the proper operation of these devices.
- Smartphones and Tablets
In the mobile computing era, rigid PCBs perform well in smartphone or tablet device. They transport power from the central processing unit to the display and the connectivity modules.
Their small size and high circuit density allow them to be used in mobile and light devices while ensuring good operation under demanding use-case scenarios.
- Consumer Electronics (TVs, Game Consoles)
From televisions to game consoles, Rigid PCBs are ubiquitous in consumer electronics, providing the essential circuitry for functionality and connectivity.
These are used as control boards for a smart TV and a game controller or a console, respectively, offering millions of users the ability to interact and enjoy.
- Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems rely heavily on Rigid PCBs to monitor and regulate machinery and processes in manufacturing, automation, and infrastructure sectors.
These PCBs assist the equipment to work accurately and monitor it for efficacy, safety, standards, and industry rules.
- Power Supplies and Medical Equipment
Power supplies and medical equipment require reliable and stable electrical circuits to deliver consistent performance and ensure patient safety.
For devices of such a class, rigid PCBs are required and usually give the essential functions of power distribution, signal processing, and control in the critical applications mentioned for power generation, medical diagnostics, and treatment.
Final Words
So that’s all you need to know about Rigid PCBs. Overall, rigid PCBs manufacture the backbone of today’s technology, be it computers or mobile phones, industrial or medical equipment; they enable things to work seamlessly and foster innovation.
So, the next time you see a gadget turning ON or the industrial equipment works perfectly fine, remember the unsung hero: the rigid PCB.