Are you confused by the complexities of electronic circuits, searching for clarity on single sided PCBs? You are not alone; most beginners do not understand what a single-sided PCB is.
But worry not, for this article is here for you. We are going to talk about everything regarding a single-layer PCB. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional PCB designer, this basic guide will help you.
What are Single-Sided PCBs?
Single-sided PCBs, or single-sided printed circuit boards, represent the fundamental building blocks of electronic devices. They have only one conductive layer that provides electrical connections for the components mounted onto them. But how do they differ from their double-sided and in some instances multilayer counterparts?
These have only one layer of conductive material and, unlike double-sided or multilayer PCBs, their complexity is therefore restricted. This simplicity brings a whole range of advantages and limitations.
Construction of Single-Sided PCBs
In the construction of single-sided PCBs, a laminate material like FR4 or fire-resistant epoxy resin with fiberglass cloth reinforcement serves as the substrate.
A thin copper foil is then etched into electrical pathways on one side of the substrate and a protective solder mask is coated to avoid unwanted solder connections.
After that, a silkscreen layer is now printed on top of the board to display component placement and other markings.
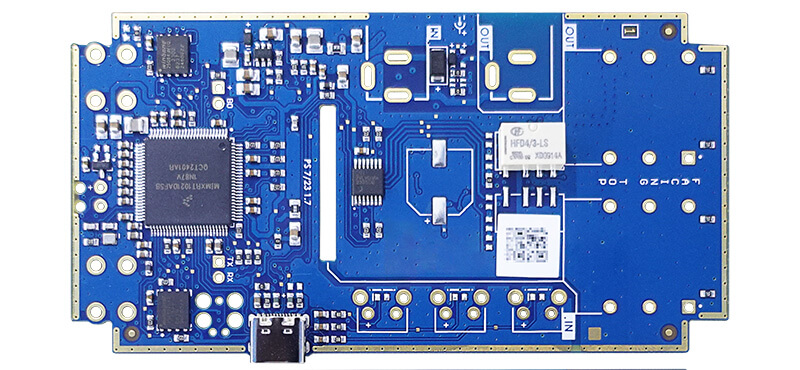
The Components of a Single-Sided PCB
The main components of a single-sided PCBs are:
- Substrate:This is the base material of single-sided PCBs and is commonly made of FR4 or a similar product that gives it its rigid and mechanical strength.
- Conducive Layer:A very thin copper foil is bonded to one side of the substrate. The copper foil is etched to form electrically conductive paths of the circuit.
- Solder Mask: It is a protective layer that would allow the copper traces to remain open, leaving bad solder connections, and would maintain the integrity of the circuit.
- Silkscreen: Overlay of components done through printing, which conveys vital information in terms of marking and placements of parts to service and assembly.
Knowing them would make you understand how the single-sided PCBs really operate, and why they are crucial to any electronics project.
On the other hand, now that you are clear with the basics of single-sided PCBs, it is now time to explain some of the limitations in detail.
Limitations of Single-Sided PCBs
Even with the simplicity and low cost of one-sided boards, they do have limitations that usually restrict their applications.
- Complexity Constraints
The single conductive layer restricts the complexity of circuits that can be implemented on a single-sided PCB. This limitation can pose challenges when designing circuits with multiple components or intricate routing requirements.
- Routing Challenges
Routing of conducting traces on a single plane can be quite challenging, especially in complex designs. Overlapping and spacing constraints between them begin to show up, and an engineer must plan these carefully to prevent signal interference and guarantee proper intended functionality.
- Limited Component Density
The single-sided nature of the PCB limits the density of components that can be accommodated. Sometimes overall efficiency and compactness of a circuit are compromised to realize larger sized boards.
- Signal Integrity Concerns
With single-sided PCBs, more of the risks exist in signal integrity issues that come from the proximity of signals or components on one layer, including crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. These can seriously affect circuit performance and reliability, especially in high-frequency applications.
Now, let’s see some of the advantages that single-sided PCBs give.
Benefits of Single-Sided PCBs
The following are the advantages of single-sided PCBs, which are the most preferable for almost all electronic applications:
- Cost-effectiveness: Inexpensive, suitable for projects operating on a really tight budget.
- Fast Manufacturing: The simplification of design will produce a reduction in manufacturing lead times.
- Easy Design and Prototyping: The low number of layers and parts facilitates design and prototyping, hence considered great for beginners.
- Suitable for Low-complexity Circuits: These devices perform best in applications having simple circuits where simplicity and cost effectiveness are requirements of the design.

Applications of Single-Sided PCBs
Some common applications of single sided PCBs are:
- Simple Calculators and Remote Controls:These devices often use single-sided PCBs because they’re cheap and easy to make.
- Low-Power Sensors and Detectors: In some cases, single-sided PCBs find use for building temperature sensors or motion detectors that do not need much power, being cost-effective and straightforward to create.
- Educational and Hobbyist Projects:Single-sided PCB is better suited for educational and classroom projects and hobbyists because it is easy to handle and work with.
- Prototyping Circuits: Most engineers prototype new circuit concepts using single-sided PCBs before refining more complicated versions. They are an easy way to make tests on the fly with little money laid out in cash.
Design Considerations
When designing a single-sided PCB, it’s important to consider:
1.Efficient Routing:
Plan your conductive traces carefully to avoid overlaps and make the most of the available space.
2.Jumper Wires for Complex Designs:
In more complex circuits, you might even be forced to use ‘jumper’ wires to allow you to connect traces on both sides of the board. It’s not ideal, but it works well as a solution.
3.Component Placement:
Place the components in such a relative position that trace lengths are at a minimum, but take care to connect them. This way you optimize the performance and reliability of your circuit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, single-sided PCBs are essential for many electronic devices and projects. They are simple and cheap, making them great for all sorts of things, from calculators to hobbyist projects.
Although they have some limits, like not being great for really complicated circuits, their benefits outweigh the drawbacks.