Have you ever faced problems relating to the VGA connector pinout? This is a common thing when connecting computers and monitors. Failure to understand it may cause connections not to work and make it difficult to troubleshoot.
But don’t you worry, because this article is going to help you out. We’re going to describe everything you need to know about VGA pinouts in simple terms. By the guide, you’ll at least have some familiarity with your VGA connectors and be able to solve any problems that might arise with them.
So, let us begin.
Understanding the VGA Connector
VGA stands for Video Graphics Array, and it is the de facto standard for transmission between computers and monitors of analog video signals. Introduced in 1987, the almost-immediate adoption of the VGA by IBM made it one of the most used due to its versatility and wide compatibility.
A VGA connector can easily be identified by its 15-pin D-sub design with three rows that contain five pins each.
Each pin in the VGA connector has a specific function, such as transmitting red, green, and blue color signals, as well as horizontal and vertical sync signals.
This pin configuration is very important to be understood for troubleshooting and to have a valid connection between devices.
Despite the rise of digital connections like HDMI and DisplayPort, VGA remains relevant in many older systems and devices.
Knowing how to use a VGA connector can become very helpful in maintenance or repair works related to older devices and also for students dealing with electronics and computer science.
Common Misconceptions Regarding VGA Pin Configuration
When it comes to the VGA connector pinout, several misconceptions can lead to confusion and frustration.
Here are some common myths and the truth behind them:
1.All Pins Are Always Used:
There seems to be a big misconception that every single pin, on a VGA connector, is always active in one way or another. The truth is, some pins might not be used or even reserved for certain purposes that don’t apply to all situations. Knowing which of the pins are important will make troubleshooting much easier.
2.VGA Is Only for Old Monitors:
Although it may be an older standard, it does not apply uniquely to ancient technology. Even with a great many modern devices—especially projectors and older laptops—the VGA connector remains widely in use. Understanding the pinout remains key to maintaining compatibility between devices.
3.All VGA Cables Are the Same:
Definitely not. There is actually a whole world of difference. Mediocre quality in cables can indeed degrade both the signal strength and image quality. Better-class cables would mostly be better shielded and have their pins configured more precisely to reduce issues.
4.Color Signals Are Mixed:
Some have the idea that, in VGA, color signals are all mixed up (Red, Green, Blue). On the other hand, each color is assigned its own respective pin to ensure that these signals are kept separated and transmitted.
By debunking these several myths, you will have a clearer view of the inner mechanisms of VGA connectors and be better equipped to tackle any issues that may arise.
Detailed VGA Pinout Explanation
Understanding the pinout of a VGA connector is essential for troubleshooting and connecting devices properly.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the 15-pin VGA connector, explaining the function of each pin:
- Pin 1 (Red Video): Carries the red video signal.
- Pin 2 (Green Video): Carries the green video signal.
- Pin 3 (Blue Video): Carries the blue video signal.
- Pin 4 (Reserved): Not used in most standard connections.
- Pin 5 (Ground): Serves as a ground for the red, green, and blue signals.
- Pin 6 (Red Ground): Ground for the red video signal.
- Pin 7 (Green Ground): Ground for the green video signal.
- Pin 8 (Blue Ground): Ground for the blue video signal.
- Pin 9 (Key/PWR): Often not connected; sometimes used for power in newer devices.
- Pin 10 (Sync Ground): Ground for the sync signals.
- Pin 11 (Monitor ID 0 / Reserved): Used for monitor identification or not used.
- Pin 12 (Monitor ID 1 / Reserved): Used for monitor identification or not used.
- Pin 13 (Horizontal Sync): Carries the horizontal sync signal.
- Pin 14 (Vertical Sync): Carries the vertical sync signal.
- Pin 15 (Monitor ID 3 / Reserved): Used for monitor identification or not used.
Visual Diagram of the Pinout Configuration:
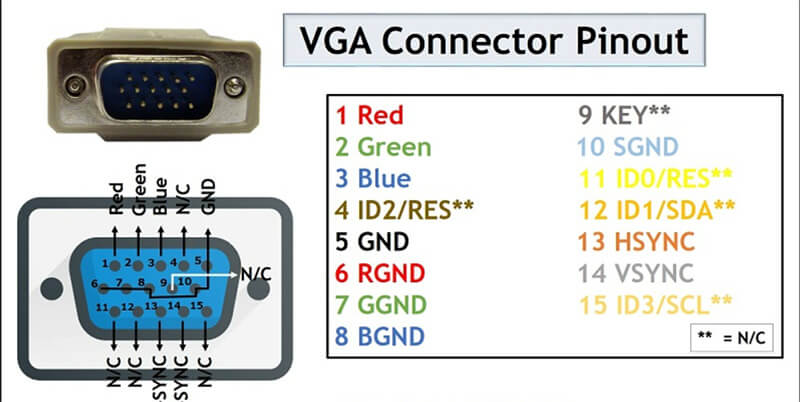
Each Pin's Function:
- Red, Green, Blue Video (Pins 1, 2, 3): These pins transmit the primary color signals that make up the video image. Each color has its own dedicated pin to ensure accurate color reproduction.
- Ground Pins (Pins 5, 6, 7, 8, 10): These are crucial for reducing noise and interference, ensuring a clear and stable video signal.
- Sync Signals (Pins 13, 14): Horizontal and vertical sync signals help synchronize the display’s refresh rate with the video signal, ensuring a stable and flicker-free image.
- Reserved/Monitor ID Pins (Pins 4, 9, 11, 12, 15): These pins are used for various purposes, including monitor identification and, in some cases, power.
Advantages of VGA
Despite being an older technology, the VGA connector offers several advantages that contribute to its continued use in various settings:
- Wide Compatibility: VGA connectors have broad compatibility with older computers, monitors, and projectors. This wide scope of compatibility makes VGA a fairly reliable choice for hooking up different devices—especially when it comes to running mixed technology.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: VGA connectors are very easy to use, and their functionality is based on the plug-and-play feature. The 15-pin D-sub connector is readily plugged or removed, so any user can do so with ease, regardless of their literacy level in computers.
- Analog Signal Transmission: The analog signal transmission of VGA can sometimes turn out to be advantageous. As an example, it may function well over long runs across cables, though the propagation of a digital signal degrades without correct amplification in such conditions.
- Cost-Effective: VGA cables and connectors are relatively low in cost compared to new digital alternatives like HDMI or DisplayPort. This cost makes VGA effective for those who want to remain within a budget or otherwise, stay practical to the user needs or organization.
- Sufficient for Many Applications: Truly not as advanced as digital connections, it is still sufficient for a lot of applications—from standard-definition video to presentations or just plain use of computers. It supports up to 1920×1080, thus making it versatile for display needs.
So these benefits point out why VGA is still relevant, specifically in those applications that combine the requirements of low cost, high compatibility, and ease of use.
Disadvantages of VGA
Even though VGA has some real advantages, it still shares a few cons, particularly in direct comparison to current digital connectors:
- Analog Signal Quality: VGA transmits only an analog signal, which badly deteriorates over long distances or through interference. Sometimes, it would even have a negative impact on the quality of the image, accompanied by ghosting, blurring, or signal noise.
- Lower Resolution and Refresh Rates: Although VGA can support resolutions up to 1920×1080, it struggles with higher resolutions and refresh rates compared to digital connectors like HDMI or DisplayPort. This makes VGA less suitable for modern high-definition and ultra-high-definition displays.
- Bulkier Connectors: Compared with most modern digital connectors, the 15-pin D-sub connector seems huge and somewhat burdensome. This can make VGA a bit less easy to work on smaller appliances or in cramped quarters.
- Lack of Audio Support: Whereas HDMI transmits both video and audio signals, VGA carries only video signals. So this means additional cables are needed to have audio, complicating the setup and the number of connections required in the setup.
These cons then make many users and manufacturers shift interest towards digital connectors, promising better performance, convenience, and compatibility with today’s electronic devices.
Different Types of VGA Connectors
VGA connectors come in a few variations. Knowing these types helps you choose the right one for your devices.
1.Standard VGA Connector

The most common type is the 15-pin D-sub, also called DE-15 or HD-15. It has three rows of five pins and is found on most computers, monitors, and projectors.
- Male Connectors: These have pins that stick out and plug into female connectors.
- Female Connectors: These have holes that receive the pins from male connectors. They are typically on monitors and projectors.
2.Mini VGA Connector

Mini VGA connectors are smaller versions used on some laptops and portable devices. They save space but have a similar pin setup.
These often need an adapter to connect to a standard VGA cable or device.
3.VGA to DVI Adapters

These adapters connect a VGA output to a DVI input, useful for devices that only support DVI (Digital Visual Interface).
Adapters can be active (converting signals) or passive (just connecting pins), depending on your needs.
4.VGA to HDMI Adapters

These adapters connect a VGA source to an HDMI display. They usually include circuitry to convert the analog VGA signal to a digital HDMI signal.
Some adapters also have an audio input since HDMI carries both video and audio, unlike VGA.
5.VGA to Component Video Adapters

These adapters convert VGA signals to component video, which is useful for older TVs or devices that support component input.
They may need specific settings to ensure proper signal conversion.
6.VGA Splitters

VGA splitters send a single VGA signal to multiple displays. They can be passive (simple cable splitters) or active (powered splitters that boost signal strength).
Active splitters are better for keeping signal quality across multiple displays.
Troubleshooting with VGA Pinout
Understanding the VGA pinout is invaluable for troubleshooting common issues and ensuring smooth connections between devices. Here’s how knowing the pin configuration can help:
- Identifying Connection Problems: If your VGA connection isn’t working, checking the pinout can reveal if a pin isn’t properly connected or if there’s a loose connection. For example, a missing ground connection (like Pin 5) can cause signal issues and affect image quality.
- Color and Image Problems: If your display shows incorrect colors or lacks clarity, the pinout can pinpoint which color signal (red, green, or blue) might be affected. Checking the corresponding pins and grounds can help diagnose and fix these issues.
- Pinout Verification: When setting up new equipment or troubleshooting existing connections, verifying the pinout ensures that you’re using the correct configuration. This prevents errors and ensures compatibility between devices.
- Testing with Multimeter: Using a multimeter to test the continuity between pins can verify if each pin is functioning correctly. This method is useful for detecting short circuits or open circuits that could disrupt signal transmission.
- DIY Solutions: Armed with pinout knowledge, you can create custom VGA cables or adapters tailored to your specific needs. This DIY approach can save costs and provide solutions not readily available commercially.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the VGA connector and its pinout is crucial for anyone dealing with video connections. Despite its age, VGA remains widely used because it’s compatible with many devices, easy to use, and affordable.
By knowing VGA pinouts well, you can troubleshoot and set up displays more effectively, whether for old or new equipment.