Are you confused between PCB and PCBA? You are not alone in this, as understanding the difference between these two is a little hard for many, but they are widely used in electronics.
Knowing this difference is important whether you are a hobbyist, a student, or a professional in the field. Do not worry, though; this article is here to help.
We will break down the concepts in simple terms, making it easy to see the roles and importance of both PCBs and PCBAs. By the end, you will know how they differ, and how each plays a vital part in an electronic device.
So, let’s get started.
What is a PCB
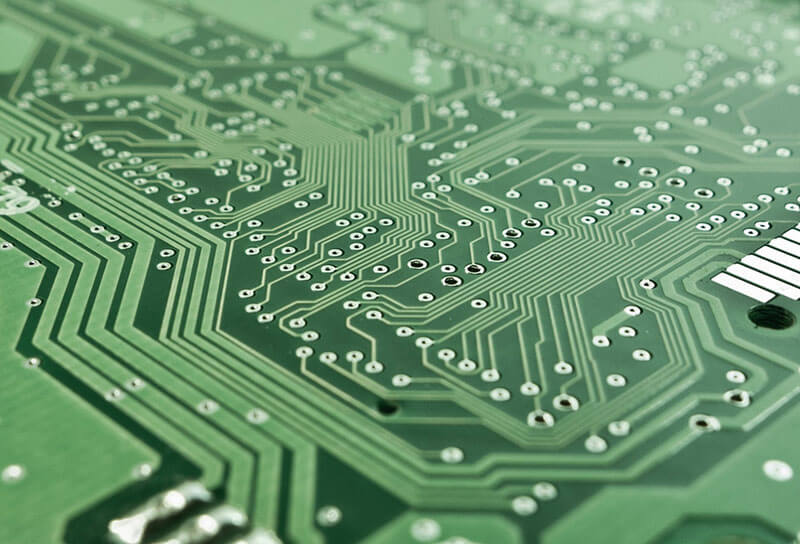
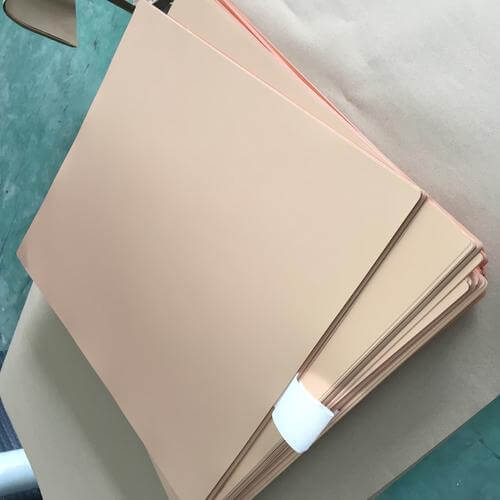
A Printed Circuit Board or PCB is a physically supporting wiring board with an insulating layer made of a thin laminated board, usually made of fiberglass, with conductive tracks made of copper etched on its surface. These tracks create pathways for electricity to flow between electronic components connected to the board.
On the body traces, conduction paths are created on its face to transfer power between the electronic components connected to it.
The PCB is one of the most critical parts of modern electronics and is the backbone for the vast majority of electronic devices in use. PCBs come in different types, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layered ones, adapted for miscellaneous applications.
What is a PCBA
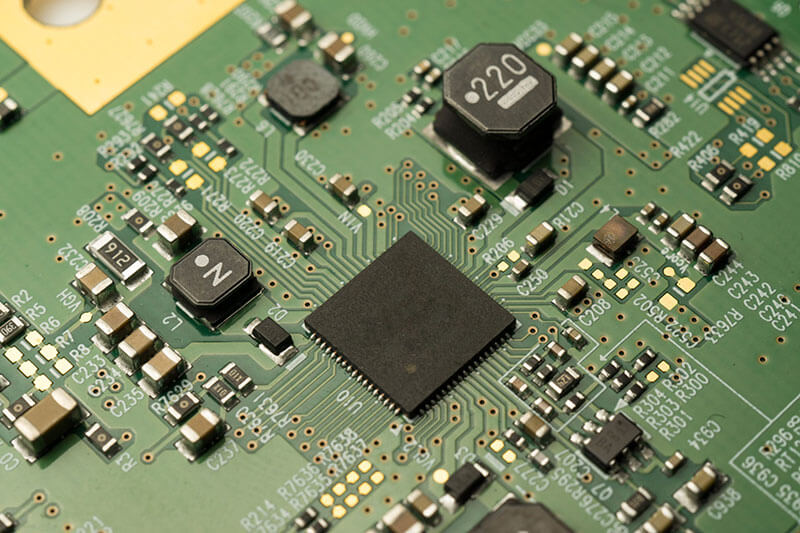
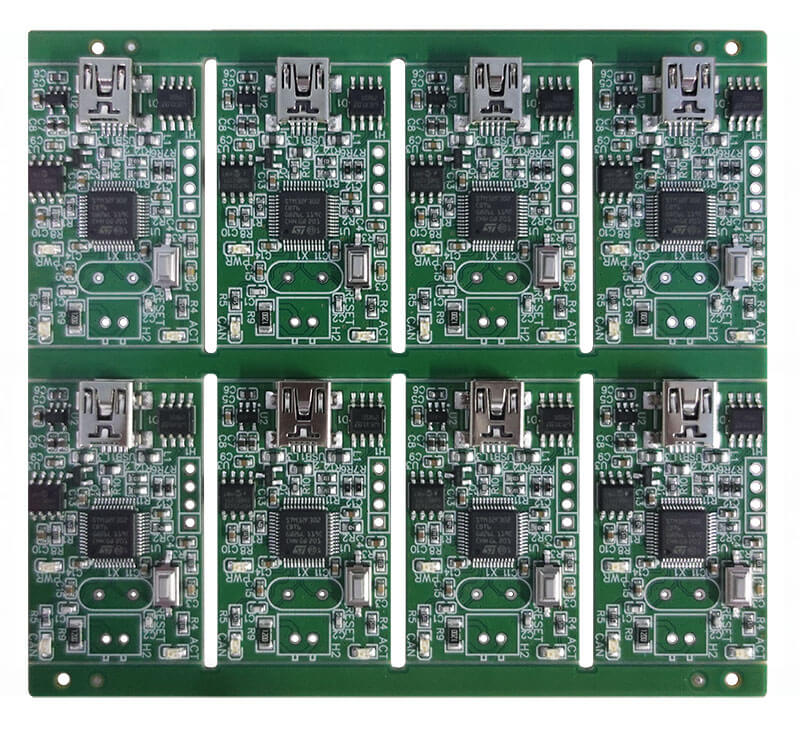
Another one is a PCBA, which stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly—a PCB with electronic components soldered onto its copper tracks.
These include resistors, capacitors, ICs, and other components that give functionality to the circuit in the end. These components are placed and soldered onto the PCB during the assembly process for them to have functionality in their intended electronic task capacity.
The combination of a PCB with attached components creates a complete electronic circuit.
Now you know the basics of both PCB and PCBA. Now it’s time to understand their differences in detail.
Key Differences Between PCB and PCBA
Following are some of the essential differences between a PCB and a PCBA:
Functionality: PCB vs. PCBA
- PCB:
A PCB is, in a simple form, a blank slate for electronic components. It is made with a nonconductive material, mainly fiberglass, in which conductive pathways are embedded or printed on the circuit board’s surface.
Elements are soldered onto the board or pads ligated to the conductive pathways. But a PCB, on its own, can’t do anything. Without components, it can’t perform any kind of electronic function.
- PCBA:
On the other hand, a PCBA is an already assembled and functional electronic circuit. Also, it will include a PCB as the base but with different electronic elements soldered on top of it.
Typically, the parts consist of resistors, capacitors, diodes, or ICs, and all the components are brought to bear to give specific electronic functions. In short, the PCBA is finally the product that will be put into electronic devices to provide the needed function.
Components: PCB vs. PCBA
- PCB:
A PCB in its simple form does not have any component installed on it. It is just the board with conductive tracks and pads where the components eventually will be put. The PCB serves to provide the framework on which these components are supported and connected but does not, by itself, perform any operations.
- PCBA:
In a PCBA, electronic components are carefully placed and soldered onto the PCB. This process involves attaching components such as microchips, resistors, capacitors, and other electronic parts to the board.
The soldering process creates a reliable electrical connection between the components and the copper tracks on the PCB, enabling the assembled board to function as an electronic circuit.
Stage of Manufacturing: PCB vs. PCBA
- PCB:
The printed circuit board is just a holding or interim stage in the electronics manufacturing process; it is prepared and ready for the installation of components but not yet to be a complete functional circuit.
Preparation of the PCB includes board layout design, etching of the copper tracks, and preparation of the board for the placement of components.
- PCBA:
The PCBA is the final assembly product. It is the fully assembled, made-with-components, and tested board ready for use as an element of electronic devices. During this stage, parts are typically placed onto a PCB’s surface and then soldered onto that surface; then very stringent Tests are done to ensure that the board works as expected.
Many boards do not pass these tests, but if the PCBA produced passes, then it will become a handy item used today within electronics applications.
In short, the key differences between a PCB and a PCBA lie in their functionality, the presence of components, and their respective stages in the manufacturing process. A PCB is a bare, non-functional board, while a PCBA is a complete, functional electronic circuit with components soldered onto it.
Understanding these distinctions is indispensable for anyone who works with electronic circuits and devices.
Now, let’s talk about some typical applications for PCBs and PCBAs.
Applications of PCBs and PCBAs
Some of the critical applications related to PCBs and PCBAs are given below:
1)Smartphones and Tablets
- PCBs: This is the backbone of both smartphones and tablets. These are the building blocks on which mounting of all constituent parts is executed, such as processors, memory modules, and communication interfaces like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular.
- PCBAs: In smartphones, PCBAs include the main logic board (motherboard) where all critical components like the CPU, GPU, memory chips, and power management circuits are assembled and interconnected.
2)Computers and Laptops
- PCBs:Most of the circuitry of a computer is composed and relies on Printed Circuit boards for connecting and supporting its parts–CPUs, GPUs, RAM modules, and storage devices (SSDs, HDDs).
- PCBAs: One of the most common examples of a PCBA can be the motherboard inside your computer/laptop. Embodied within it are complex circuits which cater to data flow, power distribution, and peripheral connectivity.
- Medical Equipment:
- PCBs:PCBs control and process signals to and from sensors for actuators in the medical world, ensuring the correct operation of ultrasound machines, ECG monitors, and patient monitoring systems.
- PCBAs: These devices have integrated PCBAs that allow accurate data processing, signal amplification, and control features, paramount in health diagnostics and treatments.
3)Automotive Electronics
- PCBs:PCBs find functions within vehicles for an array of technologies, among them engine control modules, dashboard electronics, electronic navigation, and entertainment centers.
- PCBAs: PCBAs convey the management of functions like engine timing, fuel injection, brake systems, and climate control within automotive electronics—issues, therefore, that affect vehicle safety, efficiency, and comfort.
4)Consumer Electronics
- PCBs: PCBs are components of televisions, home appliances, such as microwaves and washing machines, and gaming consoles for connectivity, control circuits, and power distribution in the devices.
- PCBAs: These devices incorporate PCBAs, which perform specific functions such as video processing, interpretation of sensor data, and user interface control.
5)Industrial Equipment and Control Systems
- PCBs: Control logic to manage a facility’s interface control and the integration or interfacing of sensors are among the uses of PCBs in industry for automation systems and industrial.
- PCBAs: PCBAs in industrial equipment provide for precise operation, data logging, and communication with central control systems to enhance productivity and efficiency.
6)Telecommunication Devices
- PCBs: PCBs are building blocks in telecommunication infrastructure, providing network connectivity, data processing, and signal routing for routers, switches, and base stations.
- PCBAs: These devices are integrated with PCBAs, capable of high-speed data handling, network management tools, and wireless communication protocols.
Choosing Between PCB and PCBA
When deciding between a PCB and a PCBA, it’s essential to understand their roles and applications in electronics manufacturing.
PCBA as the Desired End Product
- Full Functionality:This is typically the desired end-product for most users and even makers. Unlike a bare PCB, essentially a non-functional board, a PCBA would include all the necessary electrical components soldered onto the PCB. These elements enable the circuit to perform some specified functions, therefore making the PCBA ready for use in any electronic device.
- Ready to Use: PCBA eliminates the need for additional assembly steps at a company, hence decreasing manufacturing time and complexity. Undergoes rigorous testing to guarantee functionality before deployment thus reliability and performance assured in your final product.
Role of PCBs in the Manufacturing Process
- Foundation for Assembly: The PCBs offer a solid foundation, combining the path of electronic circuits, established by the non-conductive base realized by etching or printing copper traces on the surface. Individual components are then added to create electrical interconnects along those paths.
- Design and Prototyping:When it comes to design and prototyping with electronics, PCBs play a vital role. Designers use PCBs to lay out circuit components to check functionality before a project moves into mass production. In this regard, using PCBs at this stage enables perfecting designs, surfaces potential issues, and performance optimization of circuits.
- Customization and Adaptability:A PCB design would offer more room to implement customization and be adaptable to any specific design requirement. Any modifications that need to be made in the layout and configuration of the PCB designs during a given design process would allow changes to the size, shapes, and functioning of the components in such a way that they can interface with a variety of applications and devices.
- Cost-Effective Production:Having a PCB as the first step in production helps in cost-effective scaling of production. It is possible for a manufacturer to mass-produce the PCB and take advantage of economies of scale before putting it together into fully operational PCBA units.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing the difference between PCBs and PCBAs is essential for anyone interested in electronics. A PCB is a blank board with pathways for electricity, while a PCBA is a PCB with components soldered on, making it work.
This is because the PCB comes in primarily during circuit design and testing, saving money through testing during production. PCBAs are ready-to-use products designed to be used straight away in devices such as phones, computers, and medical tools.