Trying to wrap your head around PCB heat sink design? It’s a lot of work. Too many calculations go into making sure your electronics stay cool enough.
Do not worry; this article is here for your ease. By the end of this step-by-step guide, you will be well versed in handling PCB heat sink design.
So let’s begin.
Heat Transfer Principles in PCB
Before heading directly into the calculation on how to design the PCB heat sink for a PCB, one needs to understand the heat transfer principles.
The main heat transfer mode of PCBs is conduction. In this, heat is basically transferred from one point to another. It is dependent on the materials’ thermal conductivity and the thickness of the layers within the PCB.
Convection and radiation are also present, especially after the heat reaches the PCB surface, allowing it to move throughout the housing to the air or to be transferred without direct contact, respectively.
Now, let us understand what is the function of heat sink in PCBs.
The Heat Sink Function In PCB
A heat sink located on a PCB is like a car’s cooling system. When the electronic device’s components are working and create some resultant heat, a heat sink comes to the rescue to dissipate that heat in order to cool down the system.
Here’s how it does that: heat, which originates in the components, is transmitted to the heatsink and dissipated over a greater surface area.
This provides a greater surface area from which the heat can dissipate into the air, releasing the heat from the heatsink. It’s just like spreading butter on a piece of toast: the more area you spread it over, the faster it melts.
But for a proper working heat sink in PCB, there is a need of effective heat sink design. Let’s discuss it’s benefits in detail.
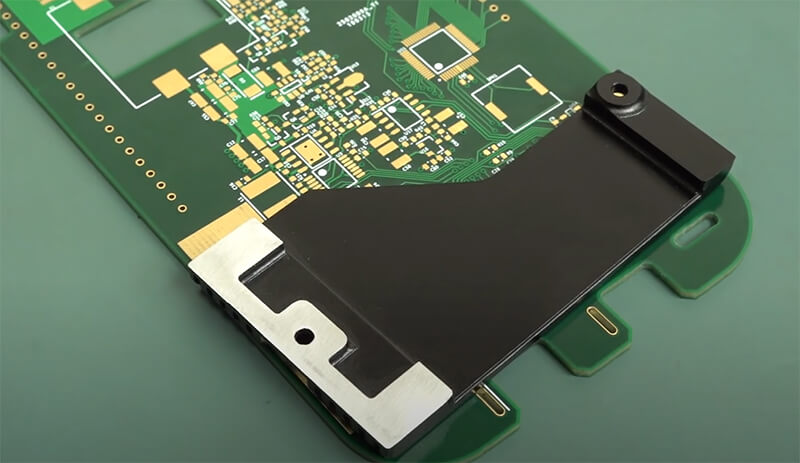
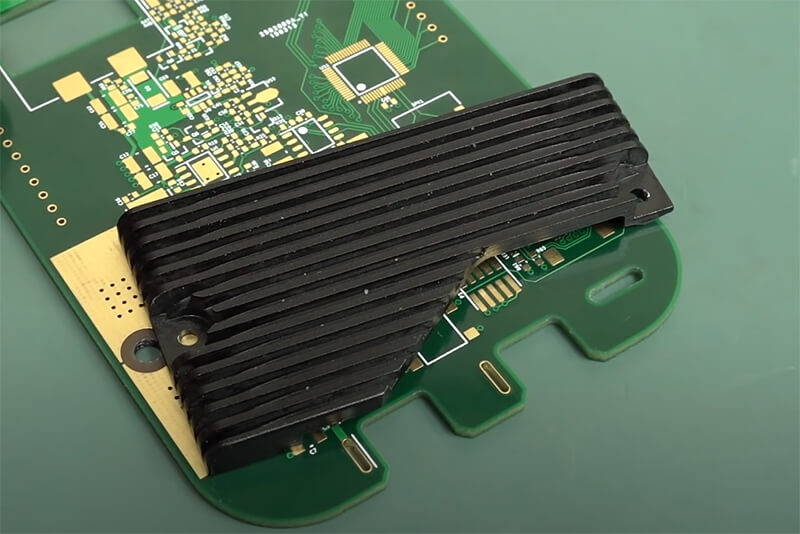

Benefits of Effective Heat Sink Design
Here are some important benefits of effective heat sink design that you must know:
- Prevent Overheating:A well-designed heat sink will protect electronic parts from overheating, allowing them to work well and significantly extend the lifespan.
- System Reliability: The fact that things don’t get very hot means that they will fail less often. Therefore, electronic systems work predictably and properly with no surprises for users because of proper heat sink design.
- Making the Product Last Long:Heat sinks help keep the components cool, which means the devices will be with you in the long run, and you will save not only in your pocket but also from the trouble of procuring replacements.
- Performance Improvement: Devices perform to the maximum when everything stays cool. Properly designed heat sinks allow electronic systems to operate smoothly, even under heavy loads.
- Lower Repair Costs:If the components don’t overheat, the probability of one of them breaking is lower, meaning that it saves you from having to spend money on replacing or repairing the components. So, good heatsink design can save you from much worry and cash in the long run.
Now you know the basics of PCB heat sink design, it’s time to learn how to calculate PCB heat sink design.
How to Calculate PCB Heat Sink Design
Here are the steps that will help you:
Step #1. Power Dissipation Estimation
First things first, we need to figure out how much heat our electronic parts are producing. This is necessary because it sets the stage of how big a heatsink should be.
We can have an approximate idea by verifying the component data sheets, performing thermal simulations, or even doing some actual testing on the setup. The idea is to be as accurate as possible here, since our calculations afterward will be on point.
Step #2. Heat Sink Thermal Resistance
Now you will have to highlight thermal resistance. It is most generally, the opposition that heat meets for conduction through a substance.
Talking of heatsinks, what we need is for them to be best at taking heat away from our components.
So we determine the complete thermal resistance from the component to the air surrounding it. In this way, we guarantee that our heat sink is going to have the ability to satisfactorily operate in any condition to keep stuff cool.
Step #3. Heat Sink Selection:
It’s super important to choose the right heat sink. We want one that can handle the heat our components are putting out.
Thus, we look for a heat sink that will give us the least thermal resistance and enough surface area to enable dissipation of the heat. Equally important is the fact that one has to choose a heatsink that is appropriate for the purpose in place: the amount of space to be occupied and the place where it will be situated.
The proper heat sink will assure that our PCB remains cool and functions in an ideal manner.
Practical Considerations in PCB Heat Sink Design
Here are some practical tips you should follow for an effective PCB heat sink design:
- Material Selection
Choose something made out of a material which can conduct heat, for instance, aluminum or copper. These are great in this application, as it can transfer heat away from your components really quickly. Don’t forget about the price, weight, and corrosion-resistance of the material.
- Heat Sink Geometry
The shape of your heat sink matters too. Adding fins might help spread the heat and cool things down faster. Select the correct form and size of a heat sink that perfectly fits your need.
- Heat Sink Mounting
How you attach your heat sink is important too. It needs to be in good contact with the components so that it can take away the heat effectively. Use the proper tools and material to attach the heat sink securely to your components.
- Airflow Considerations
Cooling, on the other hand, is all about airflow. You want to make sure there is enough space around your heatsink to provide adequate air circulation. You might need to add fans or any other cooling gadgets, just in assistance of moving the air.
Look out for dust and anything else that’s a clog to that airflow, so it doesn’t make it hard for your heatsink to do its job.
Conclusion
Understanding basic principles of heat transfer, role and advantage of heat sink, and then a process flow in calculation and selection.
These strategies of implementation provide the most effective cooling for the electronic components, maximizing the beneficial effect on the PCB’s reliability, life, and performance.