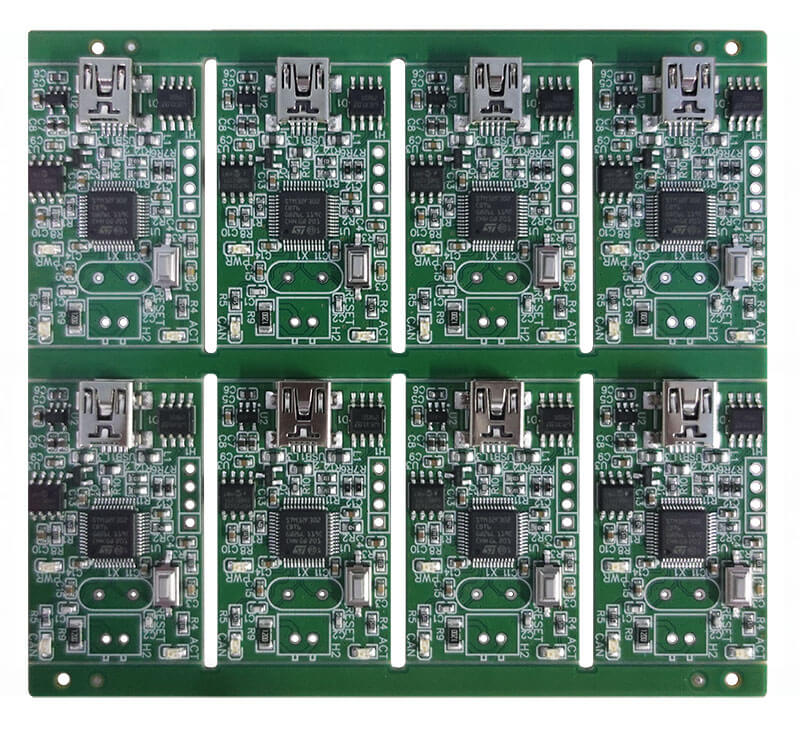
These days, miniaturization is the driving force in the electronics industry. This has led to the development of miniaturized, faster electronic gadgets with surface mount devices (SMDs) that are essential for this purpose. SMD components are designed to be placed directly on the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) using a method called Surface Mount Technology (SMT).
This technology replaced the older through-hole technique, enabling the creation of compact and reliable devices. This article will review the types of SMD components, their advantages, challenges, and applications in various electronic devices. So, let’s get started!
Types Of SMD Components
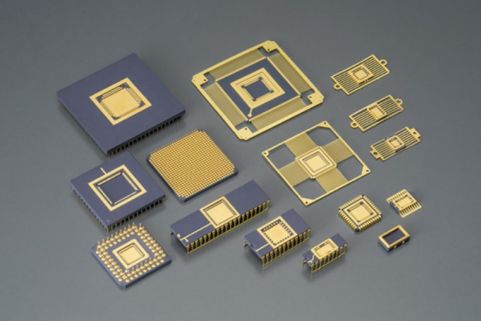
SMD components take various shapes, each with a specific use in an electronic circuit. Here are the primary types:
#1. Passive Components:
- Resistors:SMD resistors are used to reduce the current flow through them. Thick film and thin film are their primary types. Thick film resistors are usually cost-effective. Thin film resistors are more high-quality in terms of precision and stability and are used for applications where very accurate results are required.
- Capacitors: They store and release electrical energy. Some of the most common types, like ceramic capacitors, are cheap and non-polar. There are also tantalum capacitors, which are more expensive and polarized but can provide higher capacitance values and stability.
- Inductors:An SMD inductor is a passive component in electronics that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. It consists of wire-wound inductors capable of providing high inductance and current handling and ferrite bead inductors that filter out high-frequency noise.
#2. Active Components:
- Integrated Circuits (ICs):These complex devices combine multiple functions on a single chip and can include microprocessors, memory chips, power management circuits, and others.
- Diodes:Current can only pass in one direction through SMD diodes, such as rectifier diodes for power supplies, Schottky diodes suitable for high-frequency applications, and Zener diodes used in circuits for voltage regulation.
- Transistors: They increase or decrease the electronic signal. It includes bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) for amplification and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) for high-speed switching and power management.
SMD Component Packages
SMD component packages come in a variety of standardized shapes and sizes, helping to simplify the process of placing and soldering parts onto PCBs. Some of the common industry standard codes are 0201, 0402, SOT-23, and BGA (Ball Grid Array).
- 0201:Measures 0.02 inches by 0.01 inches – typically for minimal space components like resistors and capacitors.
- 0402: These components measure 0.04 by 0.02 inches and cover small-ranged components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors
- SOT-23: Measures about 0.11 by 0.09 inches and is usually used for simple transistors and diodes.
- BGA (Ball Grid Array):It is designed for ICs and larger complex components consists of an array of solder balls for high-density connections, easier routing and better heat dissipation.
The package-to-component size/value/function relationship is paramount. Smaller packages like 0201 and 0402 are ideal for passive components with little power requirement. However, larger packages like SOT-23 and BGA are preferred for elements needing more connections or higher power dissipation.
Advantages Of SMD Components
SMD components have several advantages as follows;
- Miniaturization:SMD parts are significantly smaller than through-hole components, allowing for more compact, smaller electronic products.
- Higher Densities: They can be placed on either side of a PCB, which allows for more components within a given area and increases functionality.
- Improved Performance: In some cases, SMD components can outperform their larger counterparts by operating faster and more efficiently.
- Automated Assembly: The assembly process leads to more accurate and reliable results. Pick-and-place machines ensure precise placement and secure mounting of components.
Challenges Of SMD Components
Despite their advantages, SMD components come with challenges:
- Smaller Size: These require delicate handling and soldering techniques due to their size.
- Inspection Difficulties: They are tiny in size; hence it is very difficult to identify faults visually.
- Limited Reworkability:Removing or repairing SMD components can be difficult and often necessitates specialized equipment.
- Higher Initial Cost:Setting up an SMD assembly line requires an initial investment in specialized equipment compared to through-hole technology.
Soldering SMD Components
Soldering SMD components varies depending on your experience level. Here are the methods for beginners and hobbyists.
Important Safety Note: When hand soldering, it is important to use lead-free solder and work in a well-ventilated area, wearing proper safety equipment like a mask or respirator to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- For Beginners:Reflow ovens are typically used for soldering SMD components in a professional setting. The solder paste is melted, creating a secure connection with the PCB.
- For hobbyists: Hand Soldering Techniques can be employed with tools like fine-tip soldering iron and solder paste. This work should only be done with proper safety equipment, such as a mask/respirator, and in a well-ventilated area.
Applications Of SMD Components
Due to their small size, these SMD components find a wide range of use in different sectors due to their better connection.
- Consumer Electronics: SMD components in things like smartphones, laptops, tablets and wearables make those devices better than they were before.
- Computers:SMD components are mostly applied in motherboards, graphics cards, and memory modules to ensure better performance and stability of products.
- Industrial electronics: It is also very important for use in industrial applications where precision and durability are key. Used in control systems, medical devices and communication equipments.
Conclusion
SMD components are a cornerstone of modern electronics, enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient, and reliable devices. If you are a professional or an enthusiast, it is important to be familiar with this type of component. By understanding both the benefits and challenges of SMDs, you can push the boundaries of electronic design and innovation.